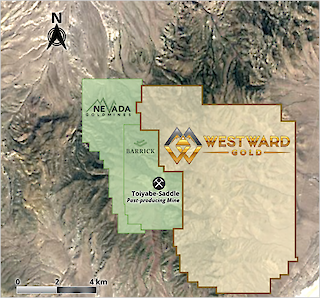
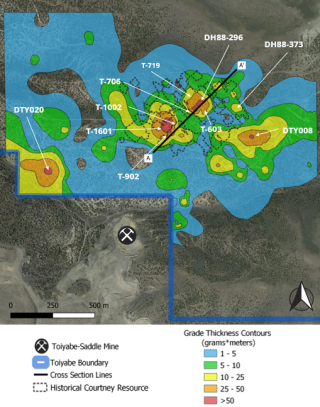
The Toiyabe Hills Project is an exploration asset consisting of 6,073 hectares of public land, administered by the Bureau of Land Management (737 unpatented mining claims). Westward has developed the potential to make a significant new discovery through years of diligent land consolidation, the application of systematic field programs, geophysical surveys, and legacy data review.
Other highlights include:
- Favourable stratigraphy associated with anomalous gold at surface and in drill intercepts
- Existing targets untested laterally and at depth
- Untested targets associated with surface geochemical anomalies, favourable stratigraphy, and structural controls
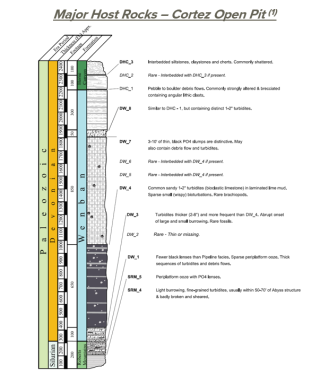
(1) NI 43-101 Technical Report, IM Exploration Inc., Prepared by Donald E. Cameron, P.Geo, August 5, 2021